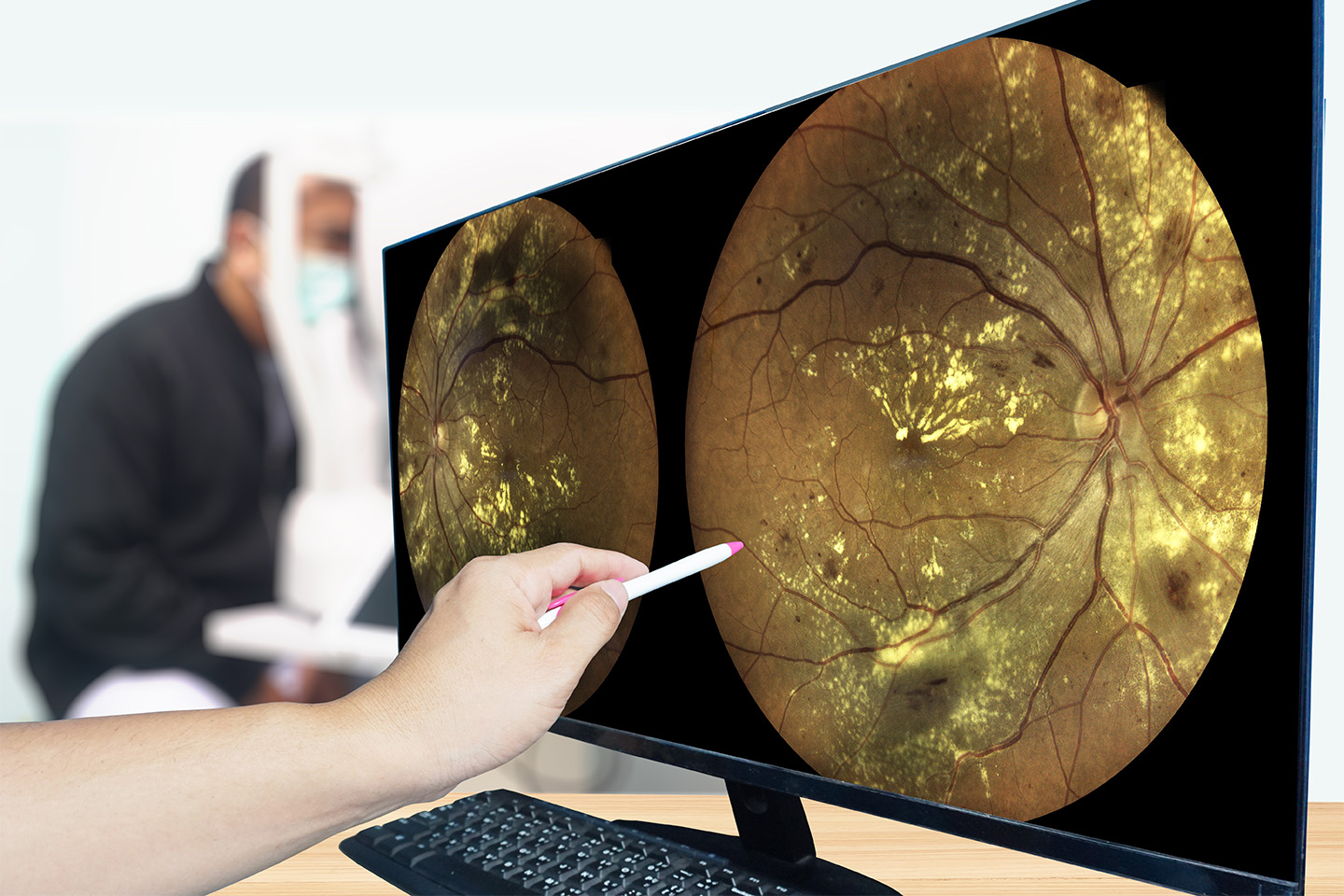
Ophthalmology Clinical Research Studies: What Are They & Why Participate?
Expert ophthalmic surgical centers will sometimes participate in national clinical research trials in order to further the scientific progress made in surgical and non-surgical treatments for vision or other eye problems. This can benefit their patients, the surgeons involved, and the clinic that is participating.
What is Clinical Research?

The National Institutes of Health define clinical research as:
“Clinical trials are part of clinical research and at the heart of all medical advances. Clinical trials look at new ways to prevent, detect or treat disease.”
Simply put, this includes all kinds of clinical research to determine the causes, effects and treatments of everything from illness to aging, medicines to holistic healing, new medical devices, types of therapies and virtually any other science that involves the study of how life works and how to help life work better. Clinical research can involve “clinical trials”. These trials involve something called a “control group”. A control group consists of the subjects that receive either no treatment or a placebo treatment while another group, ”the treatment group” or ”the treatment arm” as it is sometimes called, receives the therapies or substances being studied. These types of studies can vary wildly depending on the goals and objectives behind them.
Clinical Research in Ophthalmology
Literature describing ophthalmology-based clinical trials will first list the objectives of the particular study. These goals can include things like the ability to evaluate the effectiveness of treatments as regards to:
- Increased quality of life after treatment and any changes for the better or worse over time
- Changes to vision or eye health both directly after treatment as well as over time
- Comparison studies of different treatments among disparate groups according to scientifically relevant factors. These can include things like age, gender, race, economic status, environmental conditions, as well as other predetermined demographic information to be considered when choosing test subjects for a clinical trial.
There are usually 4 types of clinical trials. These are broken down into phases. Most new treatments and tests go through 3 phases before gaining approval from the FDA.
- Phase I clinical trials: tests part of the new treatment in a small group of people to see if the methods are safe and cause any side effects.
- Phase ll clinical trials: tests the complete treatment in a still larger group with more variables.
- Phase lll clinical trials: tests a very large group of the general population in order to learn as much as possible about the effects of the new treatment in a large demographic population.
- Phase lV clinical trials: continue to test even after approval by the FDA.
Why is Clinical Research in Ophthalmology Important
There are approximately 300 million people living in the world today who experience vision impairments, including blindness, and who need treatments ranging from corrective surgery to other non-invasive treatments. Clinical research is one of many tools that can help lead to treatments and therapies that can help make their quality of life better. These trials help researchers discover innovative ways to prevent, treat, and test for diseases by developing new:
- Medicines
- Procedures like surgeries
- Diagnostic tools
- Disease prevention regimens
- Vaccines and serums
- Over the counter and prescription eye drops
- Other treatments, therapies, and therapeutics to treat vision or other eye problems
Researchers recruit healthy volunteers to join research studies. These study participants are separated into a treatment group and a control group. The treatment group receives the new therapy, and the control group receives either the standard treatment or a harmless placebo with no effect. This is almost always a “double masked test study”. This simply means the test subjects and researchers are both unaware of who receives the real treatments and who receives the placebo or standard treatment.
Depending on the trial, volunteers may be asked to do things like:
- Take eye exams
- Take pills, eye drops, or ointments
- Go to follow up appointments over several months or even years to determine the amount of success of the treatment being studied
A most recent example of an important ophthalmic research study has been related to COVID-19 and the use of daily eyewear (glasses) and the susceptibility of the disease. Other ongoing research includes people with a history of COVID-19 disease and the impact on their vision.
Why Should You Participate In an Ophthalmic Clinical Trial
Taking an active role in ophthalmic clinical research projects is a great way to help countless numbers of people in the future. Volunteers are urgently needed for this valuable work. It’s only through your involvement that researchers can develop new treatments to combat, diagnose, heal or prevent eye disease.
How to Get Involved with Ophthalmic Clinical Research Trials at ICON Eyecare in Grand Junction
The eye doctors at ICON Eyecare in Grand Junction are active participants in national clinical trials involving eye diseases and how to better treat them. Our clinic is invested in exploring methods beyond standard treatments to improve non-surgical and surgical methods for better outcomes for our patients and the public in general. We work through partnerships with medical industries and pharmaceutical companies that produce new drugs, drops, vision correction devices, and artificial lenses.
Because we’re committed to improving our patients’ quality of life through better vision and eye health, and we’re involved in advanced research trials, we have access to new research treatments not yet available to the public.
We invite our patients to become study participants in the research trials at ICON Eyecare which helps improve their outcomes and helps others by contributing to medical breakthroughs.
Every research study goes through an internal review process. Ask your ICON Eyecare doctor about whether you qualify for a clinical research trial.